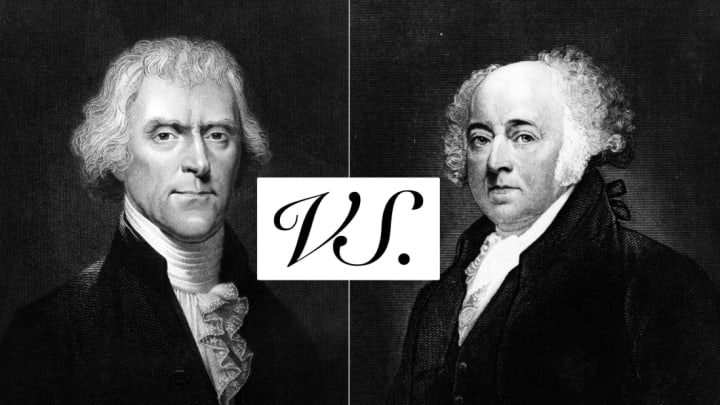
Negative campaigning in the United States can be traced back to John Adams and Thomas Jefferson. Back in 1776, the dynamic duo combined powers to help claim America's independence, and they had nothing but love and respect for one another. But by 1800, party politics had so distanced the pair that, for the first and last time in U.S. history, a president found himself running against his VP.
Things got ugly fast. Jefferson's camp accused President Adams of having a "hideous hermaphroditical character, which has neither the force and firmness of a man, nor the gentleness and sensibility of a woman." In return, Adams' men called Vice President Jefferson "a mean-spirited, low-lived fellow, the son of a half-breed Indian squaw, sired by a Virginia mulatto father." As the slurs piled on, Adams was labeled a fool, a hypocrite, a criminal, and a tyrant, while Jefferson was branded a weakling, an atheist, a libertine, and a coward. Even Martha Washington succumbed to the propaganda, telling a clergyman that Jefferson was "one of the most detestable of mankind."
JEFFERSON HIRES A HATCHET MAN
Back then, presidential candidates didn't actively campaign. In fact, Adams and Jefferson spent much of the election season at their respective homes in Massachusetts and Virginia. But the key difference between the two politicians was that Jefferson hired a hatchet man named James Callendar to do his smearing for him. Adams, on the other hand, considered himself above such tactics. To Jefferson's credit, Callendar proved incredibly effective, convincing many Americans that Adams desperately wanted to attack France. Although the claim was completely untrue, voters bought it, and Jefferson won the election.
PLAYING THE SALLY HEMINGS CARD
Jefferson paid a price for his dirty campaign tactics, though. Callendar served jail time for the slander he wrote about Adams, and when he emerged from prison in 1801, he felt Jefferson still owed him. After Jefferson did little to appease him, Callendar broke a story in 1802 that had only been a rumor until then—that the President was having an affair with one of his slaves, Sally Hemings. In a series of articles, Callendar claimed that Jefferson had lived with Hemings in France and that she had given birth to five of his children. The story plagued Jefferson for the rest of his career. And although generations of historians shrugged off the story as part of Callendar's propaganda, DNA testing in 1998 showed a link between Hemings' descendants and the Jefferson family.
Just as truth persists, however, so does friendship. Twelve years after the vicious election of 1800, Adams and Jefferson began writing letters to each other and became friends again. They remained pen pals for the rest of their lives and passed away on the same day, July 4, 1826. It was the 50th anniversary of the Declaration of Independence.
Kerwin Swint is a professor of political science at Kennesaw State University and the author of Mudslingers: The 25 Dirtiest Political Campaigns of All Time.